Optimizing Image Loading and Performance with fetchpriority Attribute
This guide covers how to use fetchpriority, an essential HTML attribute for optimizing image loading speedsa core part of Search Engine Optimization (SEO). Learn how to assign image loading priorities to the web browser and explore specific optimization methods to improve Core Web Vitals metrics such as First Contentful Paint (FCP) and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
Optimizing Core Web Vitals by Setting Image Loading Priorities
In text-based pages, image loading speed is a critical factor that significantly impacts overall system performance. To minimize the negative impact of images during SEO optimization, you can assign priorities to image loading in addition to file size optimization. Here is a guide on fetchpriority, an attribute that allows you to control images to enhance search optimization speed.
Usage and Importance of fetchpriority for SEO Optimization
This tag can be used alongside the existing preload attribute, providing a hint to the browser to load specified images before other elements like scripts or CSS. Since images visible in the first screen (viewport) are key measurement elements for LCP (Largest Contentful Paint), controlling the loading order of these images is vital for SEO.
Images outside the initial viewport (non-above-the-fold images) should use Lazy Loading and be assigned a lower priority to manage overall page load speed. This technique is essential for improving User Experience (UX) and reducing unnecessary resource competition.
fetchpriority Attribute Values and Usage
The fetchpriority attribute is a hint attribute that sets the priority when the browser loads an image.
The image in the first viewport is the most critical asset as it is the first thing a user sees. Therefore, you should assign the fetchpriority="high" attribute to ensure this image loads before other resources. While older browsers may ignore this attribute, it significantly contributes to performance in most modern browsers supporting web standards.
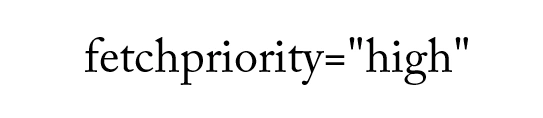
| Attribute Value | Description | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
high |
Load immediately with the highest priority | Critical images in the first viewport (LCP elements), hero banners |
low |
Load later with the lowest priority | Below-the-fold images, secondary small icons |
auto |
Use browser's default priority | General images and default value |
✔ Example: Loading a critical logo or the first image quickly
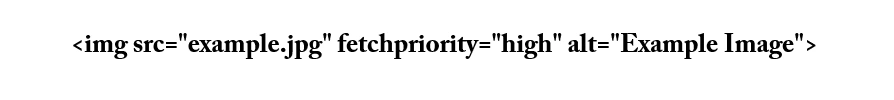
img src="main.jpg" alt="Main Image" fetchpriority="high"
Difference Between preload and fetchpriority and Combined Usage
While preload explicitly commands the browser, "This resource will be needed soon, so fetch it early," fetchpriority is a priority hint saying, "Treat this resource as more important than others when fetching it." Using preload to fetch a resource in advance while applying fetchpriority="high" to give the fetch act itself a high priority is even more effective for improving LCP.
Example: link rel="preload" href="hero-image.jpg" as="image" fetchpriority="high"
Q: Can I apply fetchpriority="high" to all images?
A: No. Applying high to all images makes it difficult for the browser to determine which resource is truly important, negating the actual performance benefits. Following the principles of page loading optimization, it is most effective to apply high only to the top 2-3 core images that must be visible to the user immediately. Other images should use low or lazy loading.
Q: Can I skip image file size optimization if I use fetchpriority?
A: No. fetchpriority controls the "loading order," not the "loading time" itself. If an image file size is large, it will take a long time to load regardless of its priority. Therefore, file size optimizations such as image compression, using WebP formats, and implementing srcset for responsive images must be done in parallel.
Q: Can I apply fetchpriority to CSS background images?
A: Yes, background images loaded via CSS can also significantly impact performance. In this case, you should typically use link rel="preload" as="image" href="bg-image.jpg" fetchpriority="high" within the HTML head tag to explicitly instruct the browser to fetch it early. You cannot use fetchpriority directly within a CSS file.